Introduction and Background
The Sesame plant [Sesamum iridicum] has been cultivated in India and the Near East for thousands of years and is now naturalized and cultivated throughout the world1. Sesame oil, which is obtained by pressing Sesame seeds, is one of the oldest known vegetal oils2. Pure, refined, pharmaceutical-grade Sesame oil is an all-natural, all-vegetal, odor-free, colorless, clear liquid. [The aromatic, brown oil typically found in oriental food stores is obtained by toasting the Sesame seeds before pressing and processing.]
Pure Sesame oil contains high levels of the natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory Vitamin E5 (alpha-, beta-, and gamma- Tocopherol) and the lignans Sesamin and Sesaminol, which explains why it is stable and resists becoming rancid 1(a)-(b),2 even though it is high in polyunsaturated fatty acids glycerides ( ~ 47% oleic and ~ 39% linoleic).
The natural antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties of Sesame oil - a consequence of its high (> 0.3 mg / mL) Vitamin E, Sesamin6 and Sesaminol6 content - is responsible for its healing powers which have been recognized for centuries3. Sesame oil has been used in traditional Chinese medicine (as an interior nasal swab) since the 16th century to relieve the discomforts associated with nasal colds and chronic sinusitis3.
Pharmaceutical companies use Sesame oil as an adjuvant1(c) in both injected or intravenous-drip medications 1(a),3. WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS PRODUCT IF YOU ARE ALLERGIC OR HYPERSENSITIVE TO SESAME PRODUCTS. NōzAmi IS 100% PURE SESAME OIL. INDIVIDUALS UNCERTAIN OR CONCERNED ABOUT POSSIBLE HYPERSENSITIVITY TO SEMAME PRODUCTS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR PHYSICIAN BEFORE USE. NOTE: THE REPORTED THRESHOLD FOR ALLERGIC REACTION TO INGESTED SESAME OIL IS 1-5 mL [see: Ann.Allergy Asthma immunol , 95(4), 11<2005>]. THE VOLUME OF SESAME OIL DELIVERED IN THE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE OF NōzAmi IS ~ 1/3 to 1/100 OF THIS AMOUNT.
Nasal Indications
As a nasal spray, Sesame oil acts (1) as a barrier to prevent the loss of moisture from the nasal lining (mucous membrane), thereby restoring the natural moisture levels to nasal passages and (2) as a softener which induces scabs, clots, hardened mucus, etc. to separate, thereby promoting their manageability. The anti-inflammatory qualities of various naturally occurring minor components of Sesame oil (see below) have been noted 3,4,6.
Individuals suffering from the discomforting effects of colds, sinusitis and associated nasal inflammation (characterized by dry, irritated, crusty nasal passages, often accompanied by bleeding or bloody discharges), have traditionally sought relief from such discomforts through the use of isotonic saline solution. However, in a recent randomized crossover clinical study designed to compare the quality of relief from the symptoms of dry mucosa, medical researchers tested isotonic saline solution against pure Sesame oil and found that Sesame oil was 3-4 times more effective than saline solution at relieving the associated dryness, crustiness and stuffiness that afflict individuals suffering from dry mucous membrane4.
Causes of dry mucous membrane are many and include, inter alia:
- Nasal inflammation and crusting associated with a cold or sinus infection.
- The use of certain nasal inhalants (particularly steroids) for hay fever.
- The effects of on-going or past-administered radiation therapy to the area of the nose.
- The use of CPAP or BiPAP machines for treatment of snoring and/or obstructive sleep apnea, even if they have been retro-fitted with humidifying devices.
- The use of oxygen therapy, particularly when introduced through nasal prongs.
- Low humidity (arid) environments, whether natural or consequenced by indoor heating or air-conditioning.
- Extended airplane travel and/or habitation at elevated altitudes.
- Following nasal surgery.
- A natural consequence of aging.
- Certain auto-immune conditions that adversely reduce or alter salivary, lachrymal and/or respiratory gland secretion.
- A condition called atrophic rhinitis.
Note: Unlike animal-derived oils which can cause Lipid Pneumonia upon inhalation, clinical studies have shown vegetal-derived oils to be SAFE to the upper and lower respiratory systems .
References
- (a) Bown, D., The Herb Society of America New Encyclopedia of Herbs and Their Uses, London, Dorling Kindersley Ltd., 2001; (b) Davidson, A., The Oxford Companion to Food, London: Oxford University Press; 1999; (c) Bruneton, J., Ed., 2nd ed. Paris: Lavoisier; 1999. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Medicinal Plants
- (a) Onstad, D., Whole Foods Companion: A Guide for Adventurous Cooks, Curious Shoppers & Lovers of Natural Foods, White River Junction, VT, Chelsea Green Publishing Co.,1996; (b) Wood, R., The New Whole Foods Encyclopedia: A Comprehensive Resource for Healthy Eating, New York, NY, Penguin Putnam Inc., 1999.
- Burden, D., Agricultural Marketing Research Center: Sesame Profile. It has been used, for example, as a balm for soothing and healing burns and minor skin eruptions2(a). In many traditional Middle Eastern societies, it is used to prevent common skin infections.
- Johnsen, J.; Bratt, B-M.; Michel-Barron, O.; Glennow, C.; and Petruson, B.; Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg., 127, 1353-56 (2001).
- A.A. Moazzami , S.L. Haese, A. Kamal-Eldin, European J. Lipid Science &Tech., 109 (10), 1022-27 (2007).
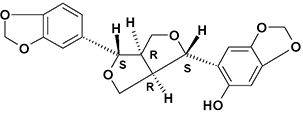
- Naturally occurring Vitamin E is composed of a mixture of Tocopherols, the most common beingthe α, β and γ Tocopherols shown below. In addition, Sesame oil contains a variety of lignans,the most prominent of which are Sesamin and Sesaminol, also shown below.
α-Tocopherol
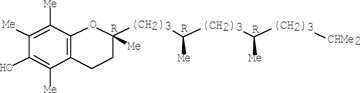
β-Tocopherol
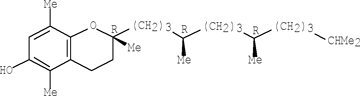
γ-Tocopherol
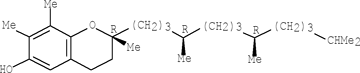
Sesamin

Sesaminol